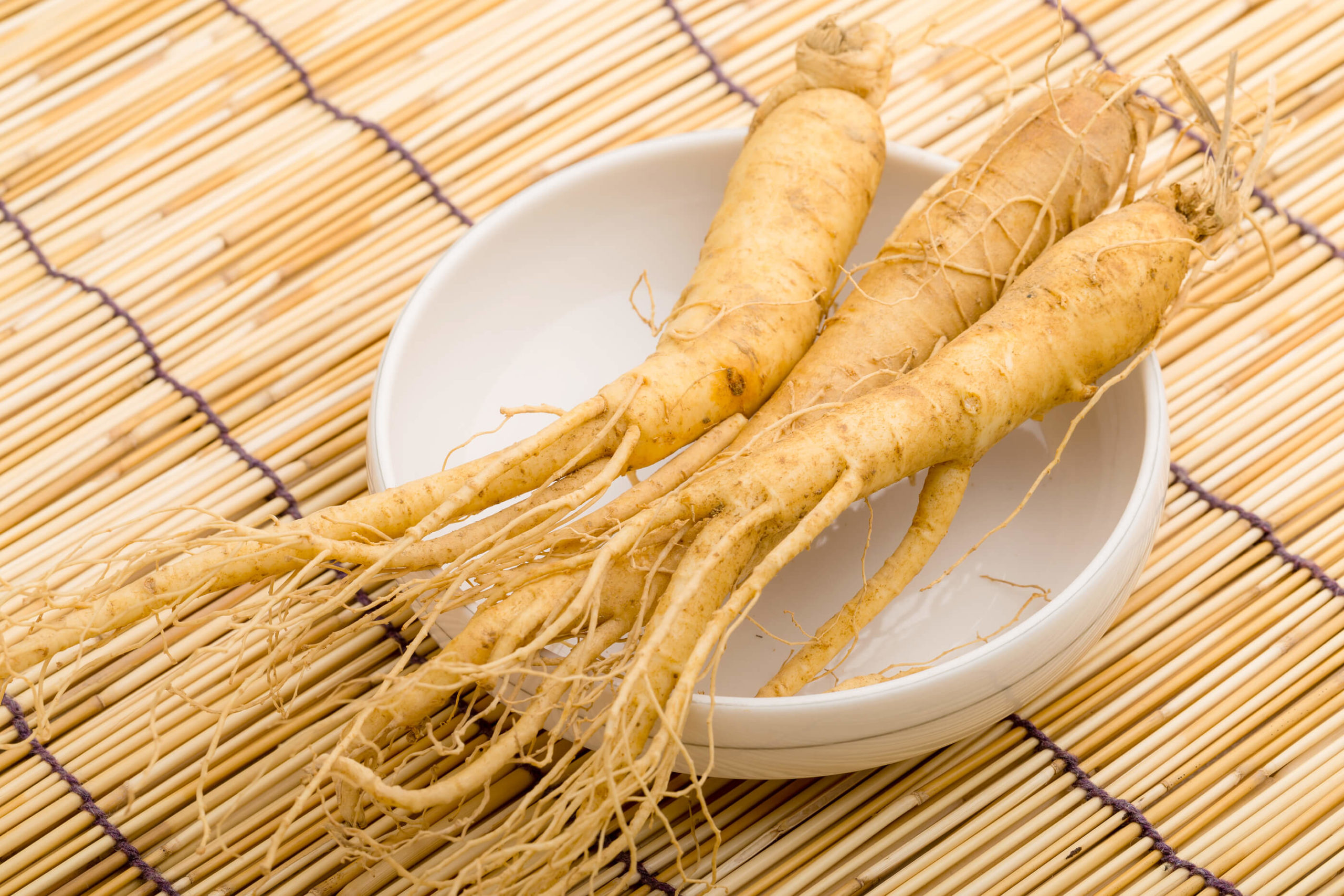
A portentous root with a peculiar look
Ginseng or, to be more precise, Panax Ginseng, the most widespread variety of this plant (and the richest in active ingredients), is a small perennial herb native to China and South Korea, about 80 cm high, consisting of a single stem that, during the flowering period (starting from the fourth year of life) presents three to six leaves and small pink flowers united in umbrella. A little anonymous plant that most people wouldn’t recognize. Its root is much better known, mainly because of its characteristic shape that recalls that of a human body. It can measure up to 20 cm in length and 3 cm in diameter. The ginseng root has been known and used for over 4000 years in Asian culture and in primarily in Chinese medicine as a very effective natural tonic, also, beneficial in boosting the production of the energy necessary to overcome stressful situations and restore inner balance.
In West culture ginseng is included in the category of adaptogenic plants. Let’s try to understand what this term stands for.
Natural adaptogen means any substance capable of increasing the ability of the body to adapt to situations of stress and weakening. In these particular situations the organism can suffer from physical and mental fatigue, weakening of natural self-defense mechanisms, emotional changes, imbalances of the various systems of the organism. Thus, an adaptogenic remedy is a substance capable of restoring balance to the organism, performing different and synergical actions.
Why is ginseng called adaptogenic? Because, containing a number of different active ingredients, it works on various systems of our organism. Triterpenoid saponins, called ginsenosides, are the main components of this root. They are attributed the adaptogenic effect of the root.
In addition to ginsenosides, several polyphenols have also been found in the ginseng root. These elements have antioxidant properties and are therefore a valid help against cellular aging due to free radical.
Ginseng also contains several essential oils, specific of this plant. According to some studies, these essential oils should have an anti-cancer effect.
Still, the ginseng root contains polysaccarides, called panaxians, that are able to lower the blood glycemic index.
Finally, traces of phytosterols, substances with activity similar to that of human hormones, were detected.
But, ultimately, what are the “practical” effects of ginseng on our bodies?
- Stimulating immune defences
- Physical performance enhancement
- Boosting mental activity and improving memory
- General mood improvement
So, we can use it to improve physical performance in anticipation of intense motor activity or simply in case of weakness; during a period of convalescence after an illness or surgery; when you are subjected to excessive mental and emotional stress; to fight cooling and influence diseases.
On the market we can find many products enriched with ginseng, such as herbal teas, coffee, gums, different cosmetic products, dietary supplements; besides of course to the root in the form of powder, dry extract, fluid extract, soft extract.
The choice of one or the other type of product to be taken will depend, partly on personal taste, partly on the specific need. Just ask an expert for advice to choose correctly.